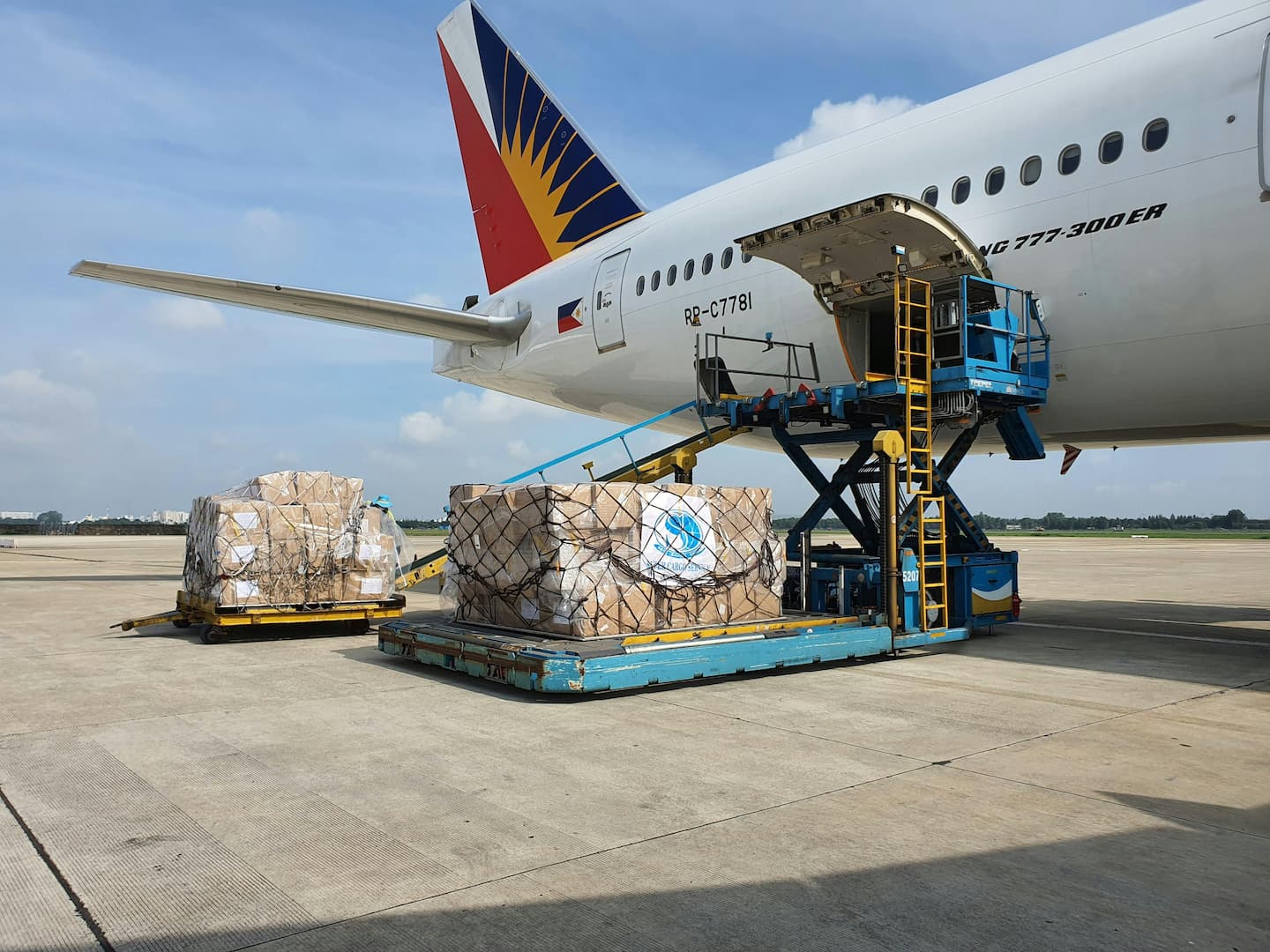
There are several ways to transport your goods and shipment from one location to another and one of them is air freight. What is air freight shipping? What are the advantages and disadvantages of transporting goods by air? In this guide, you will learn more about air freight shipping, cargo, the required documentations and rates.

What is Air Freight?
Air freight refers to the transportation of goods using an air carrier. For the quickest delivery of goods, it is the go-to choice, however, it is also the most expensive transportation mode. Air freight is a convenient method of transportation to move smaller shipments from one part of the globe to another. Businesses typically rely on air freight service for international trade due to its reliability and speedy delivery.
What is Air Cargo?
Air cargo refers to shipments that are transported by air from one place to another. There are 2 distinct types of air cargo shipments – general cargo and special cargo.
General cargo refers to items such as clothing and electronics, special cargo includes perishable goods and hazardous materials that require special handling and storage.
Advantages of Air Freight Shipping
Below are some of the advantages of shipping by air freight:
1. Fast and Timely Delivery
Air freight is the fastest mode of transport, significantly reducing transit times. This is ideal for businesses that require quick delivery to meet urgent deadlines, ensuring products reach markets promptly. The speed of air cargo shipping is unmatched, making it a preferred choice for time-sensitive goods, including perishable items and high-value products that require expedited delivery.
2. Frequent Flights
Air freight shipping services are known for their reliability, with strict schedules and frequent flights ensuring timely deliveries. This minimizes the risk of delays and helps maintain a smooth supply chain, providing businesses with the confidence that their shipments will arrive on schedule. The consistent scheduling of air cargo flights reduces uncertainty and allows for precise inventory management and planning.
3. Global Reach
Air freight connects to airports worldwide, providing extensive reach and access to international markets. This global network allows businesses to ship goods to almost any destination with ease, making it possible to tap into new markets and customer bases. Whether shipping to major metropolitan areas or remote regions, air freight offers the flexibility and capability to deliver goods across vast distances.
4. More Security
Airports have stringent security measures in place, reducing the risk of theft and damage. Air freight is a secure option for transporting high-value and sensitive goods, such as electronics, pharmaceuticals, and luxury items. The controlled environment and tight security protocols at airports and on aircraft help protect shipments from unauthorized access and potential damage, ensuring the safe arrival of valuable cargo. Customs clearance and cargo inspections are more efficient, requiring minimal handling and thus less time required for transit.
5. Real-time Tracking
You are able to track the real-time status of your cargo as most air freight service providers offer web-based tracking services.
Disadvantages of Air Freight Shipping
Below are some of the disadvantages of shipping by air freight:
- Cost: Air freight forwarding is typically costlier compared to other modes of transportation, more expensive than sea or land freight due to the high cost of fuel and airport fees.
- Weight Limitations: Compared to the large space on ships, air carriers have limited space, thus imposing strict weight and size restrictions on shipments.
- Weather Conditions: Air freight is highly dependent on the weather conditions. Extreme weather conditions like storms, fog or volcanic eruptions can lead to further delays or even cancellations.
- Environmental Impact: Air carriers contribute more to carbon emissions as they have a higher carbon footprint than other modes of transport.
- Limited Cargo Types: Some goods may be unfit for air freight such as oversized equipment or highly flammable materials.

When Should Businesses Consider Air Freight Logistics?
Businesses should consider using air freight logistics for:
- Time-sensitive or urgent shipments.
- High-value or fragile shipments like luxury items, glass bottles and items that easily break,
- Perishable goods like fresh produce, medical supplies or live animals that need to reach their destination quickly.
Documentation Requirement for Air Freight
Proper documentation is important for ensuring your goods are cleared when passing through customs efficiently and are compliant with Malaysian regulations. Having the right documents speeds up the process and also reduces the risk of delays and penalties.
Below are some required documents for air freight in Malaysia:
- Airway Bill (AWB): A mandatory document issued by the carrier or freight forwarder that serves as a receipt for goods and outlines the contract of carriage.
- Commercial Invoice: A detailed document provided by the seller that includes the description of the goods, value, terms of sale, and details of the buyer and seller. This is essential for customs clearance.
- Packing List: An itemized list detailing the contents of each package, including dimensions, weight, and quantity. This document helps in the verification process during customs inspections.
- Certificate of Origin (if applicable): A document certifying the country of manufacture of the goods. This is often required for preferential tariffs under trade agreements or to meet specific import regulations.
- Cargo Manifest: A summary document listing all cargo on a flight, including details such as shipper and consignee information. It is essential for airlines and customs authorities to track shipments.
- Customs Declaration: A declaration form that must be completed and submitted to Malaysian customs authorities, detailing the nature, value, and classification of goods being imported or exported.
- Other Relevant Documents (as required): Examples of relevant documents needed for air freight include permits for restricted goods, licenses for certain commodities, hazardous goods declarations (if applicable), or health and phytosanitary certificates for specific cargo types.
For more information on the required documentation or assistance with preparing your air freight shipment, feel free to contact us.
Factors Affecting Air Freight Rates
Air freight rates can be affected by several key factors:
1. Weight and Volume of the Shipment
Air freight charges depend on the weight and volume of your shipment. Heavy or bulky cargo will cost more to be transported by air freight.
2. Distance of the Designated Location
Depending on the destination distance, longer distances typically result in higher air freight charges.
3. Types of Cargo
Certain types of air cargo like hazardous materials or fragile items which require special handling and tighter security will cost more.
4. Item Shelf Life
Temperature-sensitive goods like fresh produce and medical supplies that need to be refrigerated will come with an additional cost due to the equipment they use inside the carriers to maintain the quality of the goods.
5. Fuel Consumption Costs
The fluctuating fuel prices can also greatly affect air freight charges.
6. Seasonality
Peak holiday seasons can increase air freight charges as there is higher supply and demand. Low season offers better air freight rates.
Challenges in Transporting by Air
When transporting goods by air, while it may be a convenient mode of transport, air freight still faces many challenges. Below are some of the challenges businesses may face with air freight:
- High Costs: Air freight is more expensive than the other modes of transportation.
- Weather Disruptions: Weather can be unpredictable. Due to adverse weather conditions such as a storm or strong winds, there may be delays or cancellations.
- Capacity Limitation: Due to the limited space available on air carriers, large or heavy shipments may be unsuitable for air cargo services.
- Regulatory Compliance: It’s crucial for businesses to comply with regulations when handling hazardous or dangerous materials. International shipping regulations vary in different regions and strict regulations are to be adhered to by the air freight industry.
- Custom Clearance: Custom clearance procedures can be tedious with the extensive paperwork involved. This can be challenging for businesses. Be sure to also be well-informed with the latest regulations to ensure there will not be any delays or cancellations.
Can Individuals or Small Businesses Benefit from Air Cargo?
Yes. Individuals or small businesses can benefit from air cargo to transport goods. Many air freight service providers offer tailored solutions for small-scale operations. Due to its reliability and speed, many individuals and small businesses choose to transport their goods by using air cargo to ensure their goods arrive safe and sound.
Partner with Global Track Lines for All Your Air Freight Needs!
Air freight is one of the go-to choices when it comes to transporting goods to other parts of the globe. Although this mode of transport can be more expensive, it is reliable, convenient and fast, ideal for global supply chains.
For a seamless logistic process, partner with Global Track Lines for air freight services in Malaysia. We provide reliable and efficient air freight solutions, including handling the customs clearance tailored to meet your logistic needs. We ensure that your goods are handled with care and delivered right on time. Contact us today for more information!